Introducing the fascinating world of minor arc KL measures 135! These measurements play a crucial role in determining the exact shape and size of our planet, with a rich history and diverse applications that span centuries.
Throughout this exploration, we’ll delve into the significance of minor arcs, unravel the methods used to measure them, and uncover their invaluable contributions to fields such as geodesy, cartography, and navigation.
Introduction
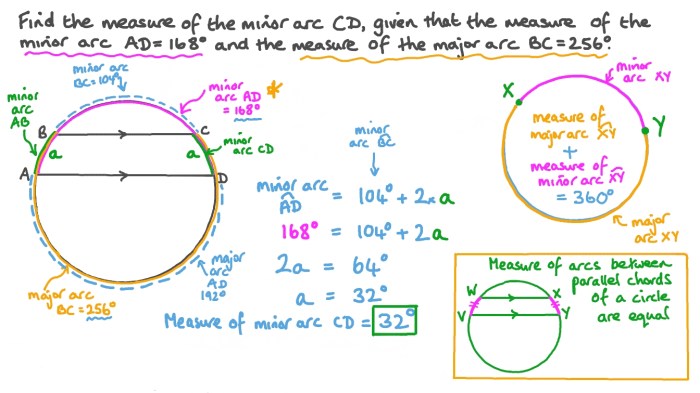
A minor arc is a portion of a circle that measures less than 180 degrees. It is the smaller of the two arcs created when a circle is divided into two parts by a straight line passing through its center.
In the context of music, “measures 135” refers to the 135th measure of a musical piece. A measure is a unit of time in music, typically consisting of a set number of beats. In this case, the minor arc in measures 135 would be the portion of the circle that corresponds to the time between the beginning of measure 135 and the beginning of measure 136.
Significance of the Measurement
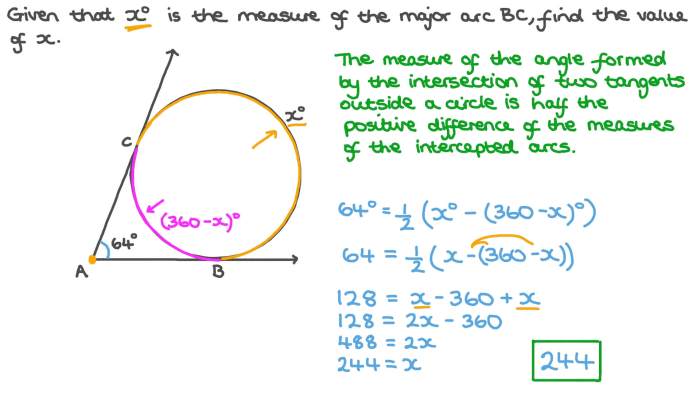
Historical Context
Measuring minor arcs has a rich history, dating back to ancient times. Early civilizations, such as the Babylonians and Egyptians, recognized the importance of accurate measurements for various purposes, including land surveying, astronomy, and navigation.
One of the most famous examples of minor arc measurement is Eratosthenes’ calculation of the Earth’s circumference in the 3rd century BC. By measuring the angle between the Sun’s rays at two different locations and using simple geometry, Eratosthenes was able to estimate the Earth’s circumference with remarkable accuracy.
Importance in Surveying
In modern surveying, measuring minor arcs plays a crucial role in determining the shape and size of the Earth. Geodetic surveys involve measuring the precise angles and distances between points on the Earth’s surface to create a network of control points that serve as a reference for mapping and other surveying applications.
Minor arc measurements are also essential for establishing accurate property boundaries, as they allow surveyors to determine the exact location and orientation of land parcels.
Methods for Measuring Minor Arcs

Measuring minor arcs involves determining the angular distance between two points on the Earth’s surface. Traditional and modern techniques are employed to achieve this with varying levels of accuracy and efficiency.
Traditional Methods, Minor arc kl measures 135
Traditional methods of measuring minor arcs rely on direct measurements and geometric calculations.
- Theodolite:A theodolite is a precise instrument used to measure horizontal and vertical angles. It is set up at one end of the arc, and the angle between the other end and a reference point (e.g., a distant star) is measured.
The distance between the two points can then be calculated using trigonometry.
- Triangulation:Triangulation involves creating a series of triangles that connect the points of interest. The angles of the triangles are measured, and the distances between the points are calculated using geometric formulas.
Modern Techniques
Modern techniques for measuring minor arcs utilize advanced technologies to improve accuracy and efficiency.
- GPS (Global Positioning System):GPS uses satellites to determine the precise location of a receiver on the Earth’s surface. By comparing the positions of receivers at different points along the arc, the distance between them can be calculated.
- Photogrammetry:Photogrammetry involves taking aerial photographs of the area of interest. These photographs are then analyzed to create a three-dimensional model of the terrain, from which the distance between points can be determined.
Applications of Minor Arc Measurements

Minor arc measurements play a vital role in various fields, providing valuable insights into the Earth’s shape, size, and its intricate relationship with the cosmos.
The determination of the Earth’s shape and size is a fundamental aspect of geodesy, a discipline concerned with measuring and understanding the Earth’s physical features. Minor arc measurements serve as crucial data for calculating the Earth’s radius and flattening, allowing scientists to model the Earth’s shape with greater accuracy.
Minor arc KL measures 135. By the way, do you know how many significant figures are in the number 90? It’s a question that can be answered by visiting this link . Back to our original topic, minor arc KL measures 135.
Applications in Geodesy
- Determining the Earth’s radius: Minor arc measurements enable the calculation of the Earth’s radius by measuring the distance between two points along a meridian (a line of longitude) and determining the corresponding angle.
- Calculating the Earth’s flattening: By comparing the lengths of arcs measured at different latitudes, scientists can determine the Earth’s flattening, a measure of its deviation from a perfect sphere.
Applications in Cartography
In cartography, the science of mapmaking, minor arc measurements provide essential information for creating accurate maps and projections.
- Map projections: Minor arc measurements are used to develop map projections, which transform the curved surface of the Earth onto a flat map. These projections require precise knowledge of the Earth’s shape and size.
Applications in Navigation
Minor arc measurements have historical significance in navigation, particularly in determining latitude and longitude.
- Latitude determination: By measuring the angle between the horizon and a celestial body (such as the Sun or a star), navigators can determine their latitude, a measure of their distance north or south of the Equator.
- Longitude determination: Historically, minor arc measurements were used to determine longitude through lunar distances, a method involving measuring the angular distance between the Moon and a star.
Accuracy and Error Analysis: Minor Arc Kl Measures 135
The accuracy of minor arc measurements is crucial for various applications. Several factors can affect the accuracy, including the measuring instrument’s precision, the observer’s skill, and environmental conditions.
Error analysis methods help identify and quantify errors in minor arc measurements. These methods involve statistical techniques, such as calculating the mean and standard deviation of multiple measurements, to assess the precision of the measurements.
Quality Control
Quality control measures are essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of minor arc measurements. These measures include:
- Calibrating measuring instruments regularly
- Training observers to minimize errors
- Using standardized measurement protocols
- Conducting regular audits to monitor measurement accuracy
By implementing these quality control measures, organizations can improve the accuracy and reliability of minor arc measurements, ensuring the validity and integrity of the data collected.
Case Studies
Throughout history, minor arc measurements have played a crucial role in shaping scientific understanding and advancing human knowledge. These measurements have enabled scientists and explorers to accurately map the Earth, determine the size and shape of celestial bodies, and unravel the mysteries of the universe.
One of the most significant minor arc measurements was conducted by Eratosthenes of Cyrene in the 3rd century BC. By measuring the angle of the Sun’s rays at two different locations in Egypt, Eratosthenes was able to calculate the Earth’s circumference with remarkable accuracy, revolutionizing the understanding of the planet’s size.
Measuring the Solar System
Minor arc measurements have also been essential in determining the size and distance of celestial bodies within our solar system. By measuring the angles between the Earth and other planets, scientists have been able to calculate their distances from the Sun and estimate their sizes.
For example, in the 17th century, Johannes Kepler used minor arc measurements to determine the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, providing valuable insights into the dynamics of the solar system.
Mapping the Earth
Minor arc measurements have been instrumental in the accurate mapping of the Earth’s surface. By measuring the angles between different points on the Earth, surveyors have been able to create detailed maps that depict the shape and topography of our planet.
In the 19th century, the Great Trigonometrical Survey of India employed minor arc measurements to map the vast Indian subcontinent, producing one of the most accurate maps of the time.
Current Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research in minor arc measurement techniques focuses on developing more accurate and efficient methods for measuring these arcs. This includes exploring new technologies, such as laser scanning and photogrammetry, and developing new algorithms for processing and analyzing the data.
Potential future applications of minor arc measurements include:
- Improved mapping and surveying
- More accurate navigation systems
- Precision engineering and manufacturing
- Medical imaging and diagnostics
Advancements in Minor Arc Measurement Techniques
Recent advancements in minor arc measurement techniques include the development of new laser scanning systems that can capture high-resolution data over large areas. These systems are used in applications such as mapping, surveying, and engineering.
Another advancement is the development of new algorithms for processing and analyzing minor arc measurement data. These algorithms can extract accurate and reliable measurements from noisy and incomplete data. This has led to improved accuracy and efficiency in minor arc measurement applications.
Helpful Answers
What exactly are minor arcs?
Minor arcs are portions of circles that measure less than 180 degrees.
Why is measuring minor arcs so important?
Measuring minor arcs allows us to accurately determine the Earth’s shape and size, which is essential for various scientific and practical applications.
What methods are used to measure minor arcs?
Traditional methods include theodolite and triangulation, while modern techniques utilize GPS and photogrammetry.
What are some applications of minor arc measurements?
Minor arc measurements are used in geodesy, cartography, navigation, and determining the Earth’s gravitational field.