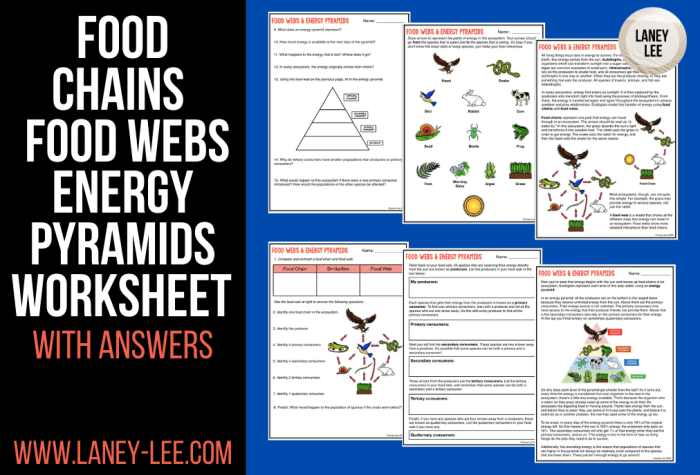
Embark on an educational journey with our captivating “Food Chains and Food Webs Worksheet.” Dive into the intricate tapestry of ecological interactions, exploring the fundamental principles that govern the flow of energy and nutrients within ecosystems. This worksheet will empower you with a comprehensive understanding of these vital concepts, fostering a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of all living organisms.
Through engaging activities and thought-provoking questions, this worksheet unveils the complexities of food chains and food webs, equipping you with the knowledge to analyze and interpret these ecological relationships with confidence.
Food Chains and Food Webs: Food Chains And Food Webs Worksheet
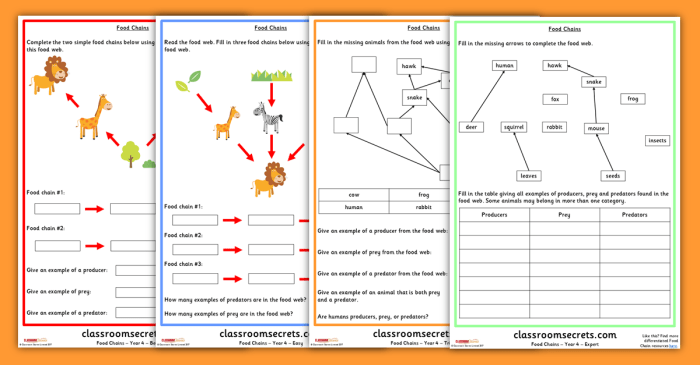
Food chains and food webs are fundamental concepts in ecology that describe the feeding relationships and energy flow within ecosystems.
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms, each of which feeds on the one below it and is in turn eaten by the one above it. A food web is a more complex network of interconnected food chains, representing the feeding relationships among multiple species within an ecosystem.
Food Chain Analysis
A food chain consists of the following components:
- Producers (autotrophs): Organisms that can produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
- Consumers (heterotrophs): Organisms that cannot produce their own food and must consume other organisms.
- Decomposers: Organisms that break down dead organisms and return nutrients to the ecosystem.
Energy and nutrients flow through a food chain in a unidirectional manner, from producers to consumers to decomposers. Each trophic level, representing a feeding level within the food chain, loses energy as it is passed up the chain.
Food Web Analysis, Food chains and food webs worksheet
Food webs are more complex than food chains and depict the interconnected feeding relationships within an ecosystem. They include:
- Multiple food chains that overlap and interact.
- Species that occupy multiple trophic levels.
- Feedback loops and interactions between species.
Food webs provide a comprehensive understanding of the dynamics and stability of ecosystems, allowing researchers to analyze the potential impacts of disturbances or changes in species populations.
Q&A
What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass, while a food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains that represents the feeding relationships within an ecosystem.
What is the role of producers in a food chain?
Producers are organisms that can create their own food from inorganic matter, such as plants that use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose through photosynthesis.
How does energy flow through a food chain?
Energy flows through a food chain from producers to consumers, with each level losing approximately 10% of the energy to respiration and other processes.
What are the different trophic levels in a food chain?
Trophic levels include producers, primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores), and tertiary consumers (top predators).