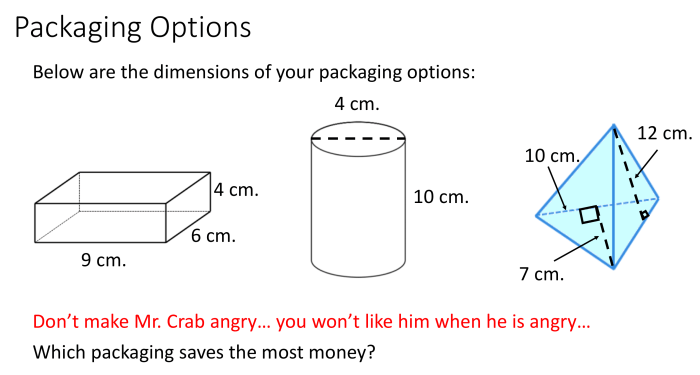
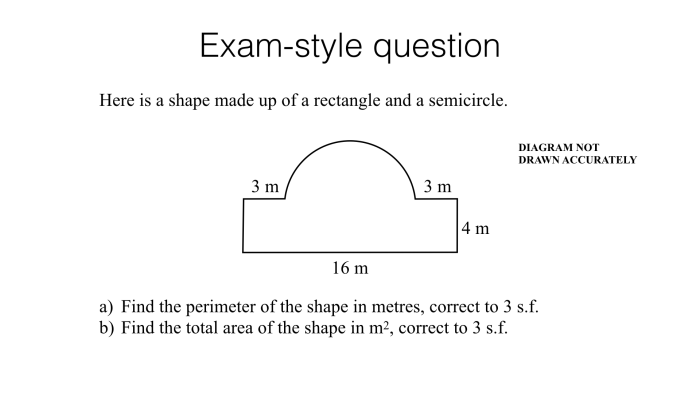
Unit 8 test polygons and quadrilaterals – Embarking on a geometric expedition, Unit 8 Test: Polygons and Quadrilaterals delves into the fascinating realm of these two- and four-sided figures. From exploring the defining characteristics of polygons to unraveling the unique properties of quadrilaterals, this test promises an immersive journey into the captivating world of geometry.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of polygons and quadrilaterals, we will uncover the relationship between the number of sides and the shape of a polygon. We will also investigate the specific characteristics and measurements associated with each type of quadrilateral, such as squares, rectangles, parallelograms, and trapezoids.
Polygons
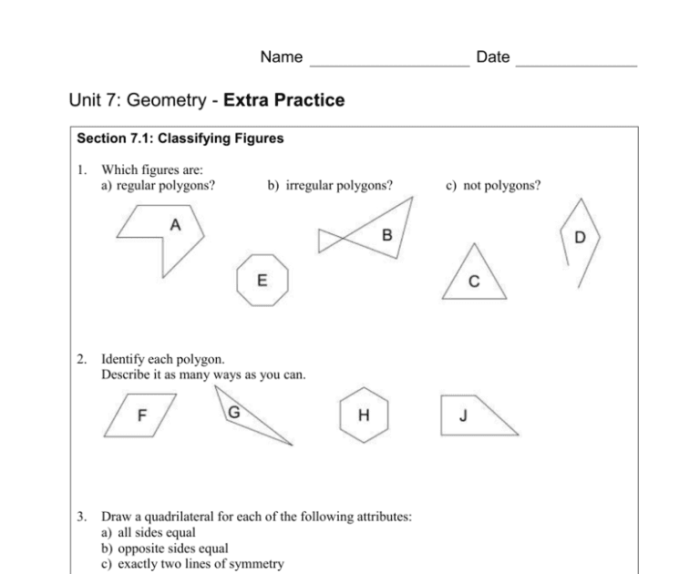
Polygons are closed two-dimensional figures made up of straight line segments. They are classified based on the number of sides and angles they possess.
Polygons are characterized by their number of sides and the regularity of their shape. Regular polygons have equal side lengths and equal interior angles, while irregular polygons do not.
Types of Polygons
- Triangle (3 sides)
- Quadrilateral (4 sides)
- Pentagon (5 sides)
- Hexagon (6 sides)
- Heptagon (7 sides)
- Octagon (8 sides)
The number of sides in a polygon determines its shape. Triangles have three sides, quadrilaterals have four sides, pentagons have five sides, and so on.
Quadrilaterals: Unit 8 Test Polygons And Quadrilaterals
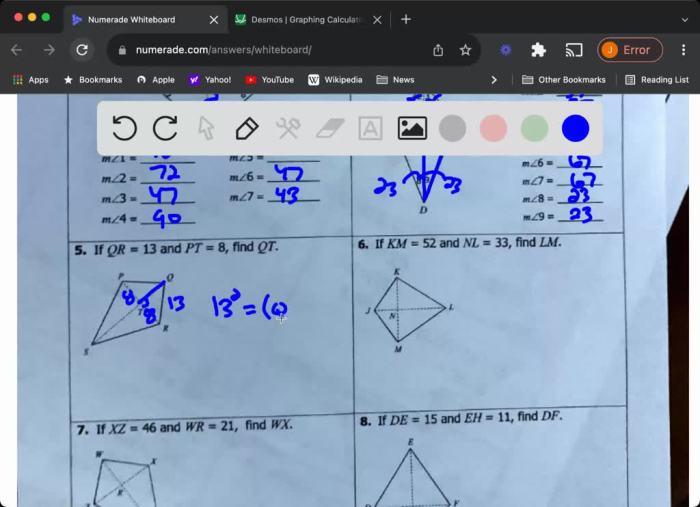
Quadrilaterals are polygons with four sides. They are characterized by their specific properties and measurements.
Types of Quadrilaterals, Unit 8 test polygons and quadrilaterals
- Square: A quadrilateral with four equal sides and four right angles.
- Rectangle: A quadrilateral with four right angles but not necessarily equal sides.
- Parallelogram: A quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and equal in length.
- Trapezoid: A quadrilateral with only one pair of parallel sides.
Quadrilaterals have specific properties associated with them. For example, squares have four equal sides and four right angles, while rectangles have four right angles but not necessarily equal sides.
Properties of Polygons and Quadrilaterals
Polygons and quadrilaterals have certain properties related to their interior and exterior angles, as well as parallel and perpendicular lines within them.
Interior and Exterior Angles
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon with nsides is given by ( n– 2) × 180 degrees.
The sum of the exterior angles of a polygon is always 360 degrees.
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
In polygons and quadrilaterals, parallel lines are lines that never intersect, while perpendicular lines intersect at right angles.
Diagonals are line segments that connect non-adjacent vertices of a polygon. In quadrilaterals, the diagonals may intersect or not.
Applications of Polygons and Quadrilaterals
Polygons and quadrilaterals are used in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design.
In architecture, polygons and quadrilaterals are used to create different shapes and structures, such as buildings, bridges, and domes.
In engineering, polygons and quadrilaterals are used to design and analyze structures, such as bridges, airplanes, and machines.
In design, polygons and quadrilaterals are used to create patterns, logos, and other visual elements.
Common Queries
What is the difference between a polygon and a quadrilateral?
A polygon is a two-dimensional figure with three or more straight sides, while a quadrilateral is a specific type of polygon with four sides.
What is the formula for calculating the sum of interior angles of a polygon?
The formula is (n-2) – 180 degrees, where n is the number of sides of the polygon.
What are the properties of a parallelogram?
Parallelograms have opposite sides that are parallel and congruent, and their diagonals bisect each other.