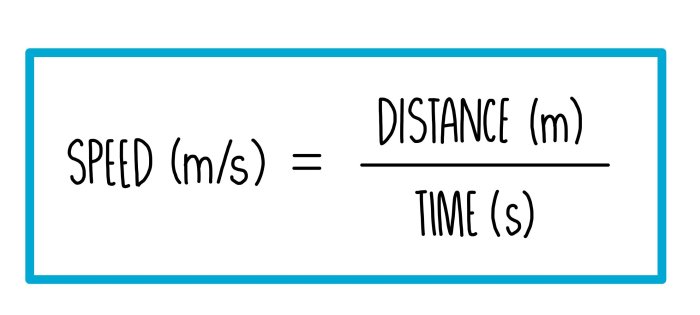Welcome to the realm of calculating speed and velocity worksheet answers, where we embark on an enlightening journey to unravel the intricacies of motion and its measurement. This comprehensive guide is meticulously crafted to provide a thorough understanding of the concepts, formulas, and applications of speed and velocity, empowering you to confidently tackle any worksheet challenge.
Throughout this exploration, we will delve into the nuances of speed and velocity, unraveling their distinct characteristics and the significance of each in describing the motion of objects. Our analysis of the provided worksheet will illuminate the key concepts and formulas employed, guiding you through the problem-solving process with clarity and precision.
Calculating Speed and Velocity: Calculating Speed And Velocity Worksheet Answers

Speed and velocity are two fundamental concepts in physics that describe the motion of objects. Understanding these concepts is essential for various applications, including engineering, sports, and everyday life.
1. Understanding Speed and Velocity
Speed is the rate at which an object covers distance, while velocity is the rate at which an object changes its position. Speed is a scalar quantity, meaning it has only magnitude, while velocity is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction.
The key difference between speed and velocity is that velocity takes into account the direction of motion, while speed does not. For example, if a car travels 60 miles per hour in a straight line, its speed is 60 mph.
However, if the car travels 60 mph in a circular path, its velocity is 60 mph in the direction of the circular path.
- Speed: If a car travels 100 kilometers in 2 hours, its speed is 50 kilometers per hour.
- Velocity: If a ball is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 10 meters per second, its velocity at the highest point of its trajectory is 0 meters per second in the upward direction.
2. Worksheet Analysis, Calculating speed and velocity worksheet answers
The provided worksheet on calculating speed and velocity covers the following key concepts:
- Definition of speed and velocity
- Formulas for calculating speed and velocity
- Units of speed and velocity
To solve the problems in the worksheet, students need to understand these concepts and apply the appropriate formulas.
- Read the problem carefully and identify the given information.
- Determine which formula to use based on the given information.
- Substitute the given information into the formula and solve for the unknown variable.
- Check the answer to ensure it makes sense in the context of the problem.
3. Sample Problems
A car travels 200 kilometers in 4 hours. Calculate the car’s speed.
Solution:
- Formula: Speed = Distance / Time
- Given information: Distance = 200 kilometers, Time = 4 hours
- Substituting into the formula: Speed = 200 kilometers / 4 hours = 50 kilometers per hour
A ball is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 15 meters per second. Calculate the ball’s velocity at the highest point of its trajectory.
Solution:
- Formula: Velocity = Initial Velocity + (Acceleration due to Gravity – Time)
- Given information: Initial Velocity = 15 meters per second, Acceleration due to Gravity = -9.8 meters per second squared, Time = 0 seconds (at the highest point)
- Substituting into the formula: Velocity = 15 meters per second + (-9.8 meters per second squared – 0 seconds) = 15 meters per second
4. Applications in Real-Life Scenarios
Speed and velocity are crucial in engineering applications, such as designing vehicles, bridges, and buildings. Engineers need to calculate the speed and velocity of objects to ensure safety and efficiency.
Speed and velocity are essential in sports, such as running, cycling, and swimming. Athletes need to calculate their speed and velocity to optimize their performance and achieve their goals.
Speed and velocity are important in everyday life, such as driving a car, walking, or riding a bike. Calculating speed and velocity helps us make informed decisions and avoid potential hazards.
FAQ Overview
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is a scalar quantity that measures the rate at which an object is moving, while velocity is a vector quantity that measures the rate at which an object is moving in a specific direction.
How do I calculate speed?
Speed is calculated by dividing the distance traveled by the time taken to travel that distance.
How do I calculate velocity?
Velocity is calculated by dividing the displacement (change in position) by the time taken to travel that displacement.