Label the indicated posterior muscles of the body and embark on a captivating journey into the intricate world of human anatomy. Understanding the anatomy of these muscles is crucial for comprehending their functions, clinical significance, and role in various body movements.
Delving into the superficial, intermediate, and deep layers of the posterior muscles, we will explore their origins, insertions, and functions, providing a comprehensive understanding of their contributions to overall body mechanics.
Posterior Muscles of the Body
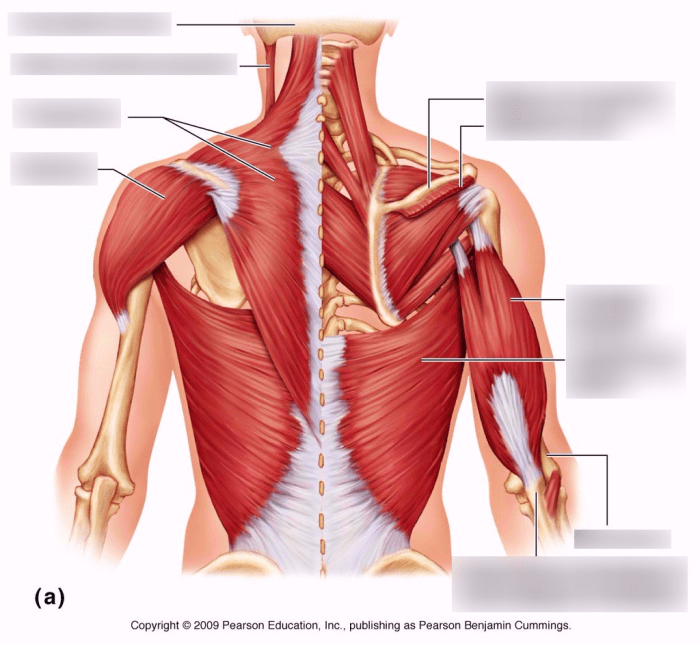
The posterior muscles of the body are a group of muscles that are located on the back of the body. These muscles are responsible for a variety of movements, including extension, rotation, and lateral flexion of the spine. They also play an important role in maintaining posture and balance.
Understanding the anatomy of the posterior muscles of the body is essential for a variety of reasons. First, it can help you to better understand how the body moves. Second, it can help you to identify and treat injuries to the back.
Third, it can help you to develop exercises that will strengthen the posterior muscles and improve your overall fitness.
Superficial Muscles
The superficial muscles of the back are the muscles that are located closest to the surface of the skin. These muscles include the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, and levator scapulae muscles.
- Trapezius muscle:The trapezius muscle is a large, triangular muscle that extends from the base of the skull to the middle of the back. It is responsible for elevating, depressing, and rotating the scapula.
- Latissimus dorsi muscle:The latissimus dorsi muscle is a large, flat muscle that extends from the lower back to the armpit.
It is responsible for adducting, extending, and rotating the arm.
- Levator scapulae muscle:The levator scapulae muscle is a small, triangular muscle that extends from the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae to the superior angle of the scapula. It is responsible for elevating the scapula.
Intermediate Muscles
The intermediate muscles of the back are the muscles that are located between the superficial and deep muscles. These muscles include the rhomboid major, rhomboid minor, and serratus posterior superior muscles.
- Rhomboid major muscle:The rhomboid major muscle is a large, quadrilateral muscle that extends from the spinous processes of the thoracic vertebrae to the medial border of the scapula. It is responsible for adducting and rotating the scapula.
- Rhomboid minor muscle:The rhomboid minor muscle is a small, triangular muscle that extends from the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae to the medial border of the scapula.
It is responsible for adducting the scapula.
- Serratus posterior superior muscle:The serratus posterior superior muscle is a large, fan-shaped muscle that extends from the spinous processes of the thoracic vertebrae to the ribs. It is responsible for elevating and rotating the ribs.
Deep Muscles: Label The Indicated Posterior Muscles Of The Body
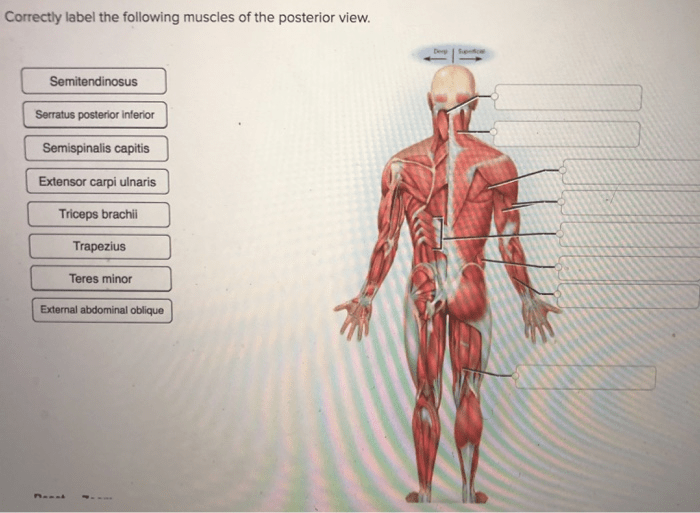
The deep muscles of the back are the muscles that are located deepest to the skin. These muscles include the splenius capitis, splenius cervicis, and erector spinae muscles.
- Splenius capitis muscle:The splenius capitis muscle is a small, triangular muscle that extends from the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae to the mastoid process of the temporal bone. It is responsible for rotating and extending the head.
- Splenius cervicis muscle:The splenius cervicis muscle is a small, triangular muscle that extends from the spinous processes of the thoracic vertebrae to the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae.
It is responsible for rotating and extending the neck.
- Erector spinae muscle:The erector spinae muscle is a large, complex muscle that extends from the sacrum to the occipital bone. It is responsible for extending the spine and maintaining posture.
Clinical Significance
Understanding the posterior muscles of the body is essential for a variety of clinical applications. For example, knowledge of these muscles can help clinicians to:
- Diagnose and treat injuries to the back
- Develop exercises that will strengthen the posterior muscles and improve posture
- Prevent and treat back pain
FAQ Insights
What are the key functions of the posterior muscles?
The posterior muscles are responsible for extending, rotating, and stabilizing the spine, as well as facilitating various movements of the shoulder, arm, and head.
Why is it important to understand the anatomy of the posterior muscles?
A thorough understanding of the posterior muscle anatomy is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal disorders, as well as for developing effective exercise programs.
What are some common injuries associated with the posterior muscles?
Strains, sprains, and tears of the posterior muscles can occur due to overuse, improper lifting techniques, or trauma. These injuries can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.