How does democracy differ from an autocracy or oligarchy? This question lies at the heart of political science, shedding light on the fundamental structures and principles that govern societies worldwide. In this exploration, we delve into the defining characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of each government type, examining their impact on decision-making, citizen participation, and societal outcomes.
From the Athenian birthplace of democracy to the rise and fall of autocratic regimes throughout history, we trace the evolution of these government systems, analyzing their historical significance and contemporary relevance. By understanding the nuances that distinguish democracy from autocracy and oligarchy, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of political systems and their profound influence on human societies.
Definition of Democracy: How Does Democracy Differ From An Autocracy Or Oligarchy
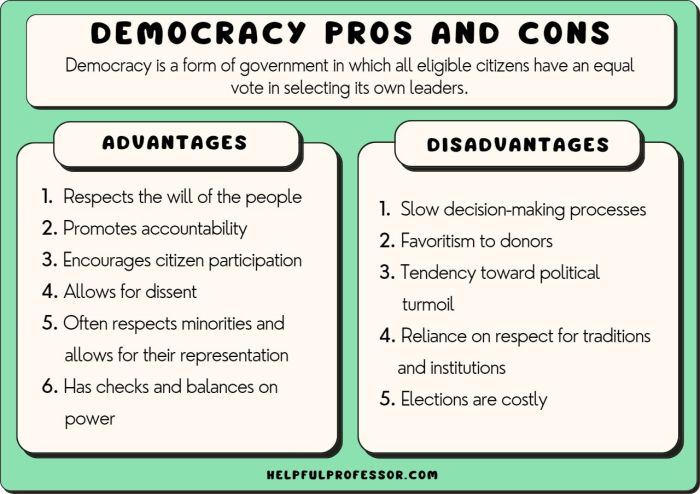
Democracy is a form of government in which the people have the power to choose their leaders and make decisions about how their society is run. The core principles of democracy include: – Popular sovereignty: The government is based on the consent of the governed.
– Majority rule: Decisions are made by the majority of the people. – Minority rights: The rights of the minority are protected. – Free and fair elections: The people have the right to choose their leaders in free and fair elections.
Examples of democratic governments include the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada.
Definition of Autocracy
An autocracy is a form of government in which one person has absolute power. The characteristics of an autocratic government include: – Centralized power: All power is concentrated in the hands of one person. – No limits on power: The autocrat is not subject to any legal or constitutional limits on their power.
– Suppression of dissent: Dissent is not tolerated and is often met with violence.
Historical examples of autocratic regimes include the Soviet Union under Joseph Stalin, Nazi Germany under Adolf Hitler, and China under Mao Zedong.
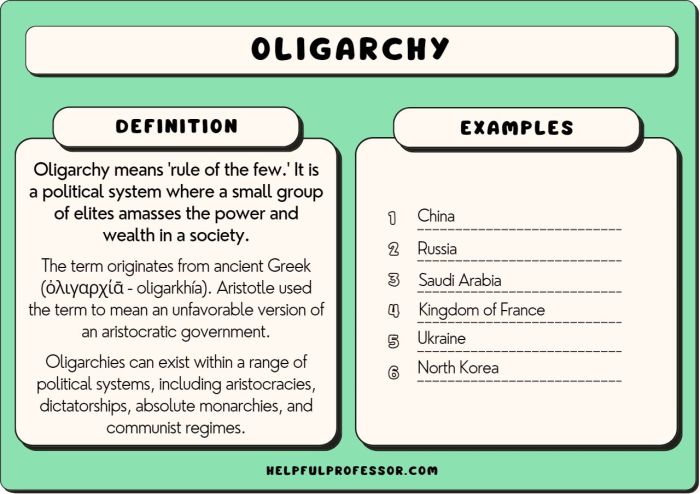
Definition of Oligarchy
An oligarchy is a form of government in which a small group of people have power. The structure and power dynamics of an oligarchy can vary, but some common features include: – Limited participation: Only a small number of people are involved in making decisions.
– Concentration of wealth and power: The oligarchs control a disproportionate amount of wealth and power. – Suppression of dissent: Dissent is not tolerated and is often met with violence.
Examples of oligarchic governments throughout history include the Roman Republic, the Venetian Republic, and the Soviet Union under Vladimir Lenin.
Key Differences between Democracy, Autocracy, and Oligarchy
The key differences between democracy, autocracy, and oligarchy can be summarized as follows:
| Characteristic | Democracy | Autocracy | Oligarchy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decision-making | Majority rule | One person | Small group |
| Role of citizens | Active participation | Passive subjects | Limited participation |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Government Type
Democracy, How does democracy differ from an autocracy or oligarchy
Advantages:
- Promotes equality and social justice
- Protects individual rights and freedoms
- Encourages political participation and accountability
Disadvantages:
- Can be slow and inefficient
- May lead to gridlock and inaction
- Can be vulnerable to demagoguery and populism
Autocracy
Advantages:
- Can be efficient and decisive
- Can provide stability and order
- Can mobilize resources quickly in times of crisis
Disadvantages:
- Suppresses individual rights and freedoms
- Can lead to corruption and abuse of power
- Can stifle innovation and economic growth
Oligarchy
Advantages:
- Can be efficient and stable
- Can provide expertise and experience in government
- Can protect the interests of the ruling class
Disadvantages:
- Suppresses the rights and interests of the majority
- Can lead to corruption and abuse of power
- Can stifle innovation and economic growth
Real-World Examples of Government Types
Democratic countries
- United States
- United Kingdom
- Canada
- France
- Germany
Autocratic governments
- China
- Russia
- North Korea
- Saudi Arabia
- Iran
Oligarchic structures
- Ancient Rome
- Venetian Republic
- Soviet Union under Vladimir Lenin
- China under the Communist Party
- Russia under Vladimir Putin
Question & Answer Hub
What is the primary difference between democracy and autocracy?
In a democracy, power is vested in the people and exercised through elected representatives, while in an autocracy, power is concentrated in the hands of a single individual or a small group.
How does an oligarchy differ from a democracy?
An oligarchy is a government in which power is held by a small, elite group, typically based on wealth, status, or family connections, while a democracy distributes power more broadly among the citizenry.
What are the key advantages and disadvantages of each government type?
Democracy promotes citizen participation, accountability, and the protection of individual rights, but it can be slow and inefficient in decision-making. Autocracy allows for swift and decisive action, but it often comes at the expense of individual freedoms and the rule of law.
Oligarchy can provide stability and expertise, but it can also lead to corruption and inequality.