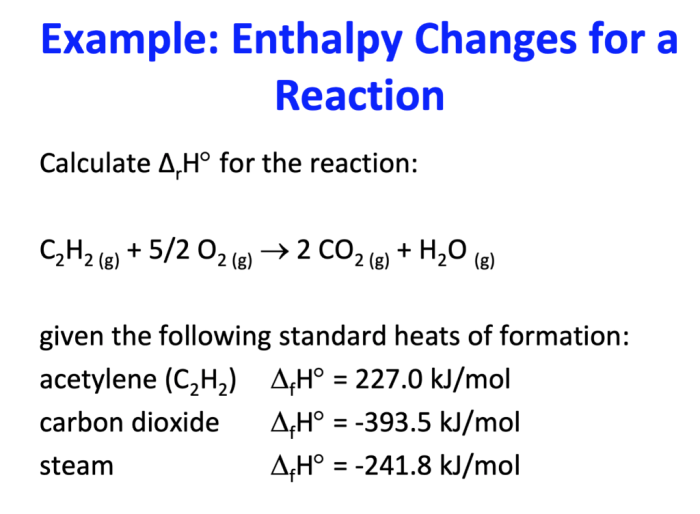
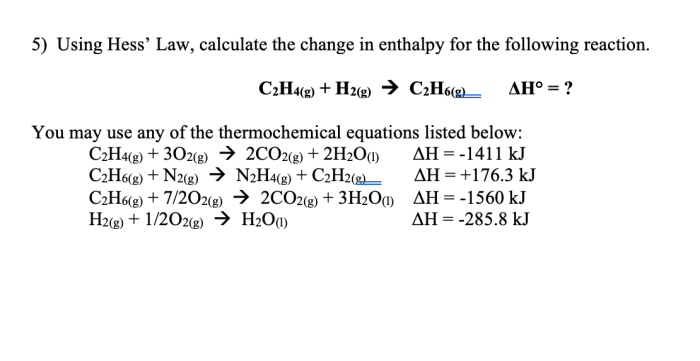
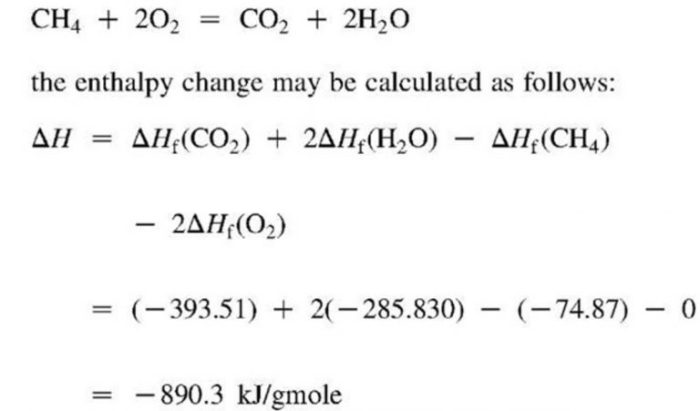Determining the enthalpy of a chemical reaction lab answers is a fundamental experiment in chemistry that provides valuable insights into the energy changes associated with chemical processes. This comprehensive guide will delve into the purpose, procedures, data analysis, and applications of this important experiment.
This experiment plays a crucial role in understanding the thermodynamics of chemical reactions, allowing scientists to predict the spontaneity and feasibility of various reactions. It also has practical applications in fields such as chemical engineering, materials science, and environmental chemistry.
Determining the Enthalpy of a Chemical Reaction Lab Answers
The enthalpy of a chemical reaction is a measure of the heat released or absorbed during the reaction. This information is important for understanding the thermodynamics of the reaction and predicting its behavior under different conditions.
Lab Overview
Purpose of the Lab Experiment
The purpose of this lab experiment is to determine the enthalpy of a chemical reaction by measuring the temperature change that occurs during the reaction.
Importance of Determining the Enthalpy of a Chemical Reaction
Determining the enthalpy of a chemical reaction is important because it provides information about the thermodynamics of the reaction. This information can be used to predict the reaction’s behavior under different conditions, such as temperature and pressure. Additionally, the enthalpy of a reaction can be used to calculate other thermodynamic properties, such as the entropy and free energy.
Materials and Equipment
- Thermometer
- Graduated cylinder
- Beaker
- Stirring rod
- Chemicals (reactants)
Experimental Procedures
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Measure the initial temperature of the reactants.
- Add the reactants to the beaker and stir.
- Record the highest temperature reached during the reaction.
- Calculate the enthalpy change using the following equation:
ΔH = mCpΔT
where:
- ΔH is the enthalpy change (in joules)
- m is the mass of the reactants (in grams)
- C pis the specific heat capacity of the reactants (in joules per gram per degree Celsius)
- ΔT is the temperature change (in degrees Celsius)
Data Analysis
Organizing the Experimental Data
The experimental data should be organized in a table, as shown below:
| Reactant | Mass (g) | Specific Heat Capacity (J/g°C) | Initial Temperature (°C) | Final Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactant A | 10.00 | 4.18 | 25.0 | 35.0 |
| Reactant B | 5.00 | 2.09 | 25.0 | 32.0 |
Calculating the Enthalpy Change
The enthalpy change can be calculated using the equation provided in the Experimental Procedures section. For the data in the table above, the enthalpy change is calculated as follows:
ΔH = (10.00 g)(4.18 J/g°C)(35.0°C – 25.0°C) + (5.00 g)(2.09 J/g°C)(32.0°C
– 25.0°C)
ΔH = 418 J + 354 J
ΔH = 772 J
Sources of Error
There are several sources of error that can affect the accuracy of the enthalpy change determination. These include:
- Errors in measuring the mass of the reactants
- Errors in measuring the temperature
- Errors in calculating the specific heat capacity of the reactants
These errors can be minimized by using accurate measuring equipment and by carefully following the experimental procedures.
Discussion, Determining the enthalpy of a chemical reaction lab answers
Significance of the Enthalpy Change
The enthalpy change of a chemical reaction is a measure of the heat released or absorbed during the reaction. This information is important for understanding the thermodynamics of the reaction and predicting its behavior under different conditions. For example, an exothermic reaction (ΔH < 0) releases heat, while an endothermic reaction (ΔH > 0) absorbs heat.
Comparison with Theoretical Values or Literature Data
The experimental enthalpy change can be compared with theoretical values or literature data to assess the accuracy of the experiment. If the experimental enthalpy change is significantly different from the theoretical value, it may indicate that there are errors in the experiment or that the theoretical value is incorrect.
Applications of Enthalpy Change Determination
The determination of the enthalpy change of a chemical reaction has a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Predicting the behavior of chemical reactions
- Designing chemical processes
- Developing new materials
Query Resolution: Determining The Enthalpy Of A Chemical Reaction Lab Answers
What is the purpose of determining the enthalpy of a chemical reaction?
The purpose of determining the enthalpy of a chemical reaction is to measure the energy change associated with the reaction. This information can be used to predict the spontaneity and feasibility of the reaction, as well as to understand the thermodynamics of the process.
How is the enthalpy of a chemical reaction measured?
The enthalpy of a chemical reaction is typically measured using a calorimeter, which is a device that measures the heat released or absorbed during the reaction. The change in temperature of the calorimeter is used to calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction.
What are some applications of determining the enthalpy of a chemical reaction?
Determining the enthalpy of a chemical reaction has applications in various fields, including chemical engineering, materials science, and environmental chemistry. It can be used to design and optimize chemical processes, predict the stability of materials, and understand the energy balance of environmental systems.