Nids is an advanced version of nips. – As NIDS (Network Intrusion Detection Systems) emerges as an advanced version of NIPS (Network Intrusion Prevention Systems), it takes center stage in the realm of cybersecurity. This transformative evolution marks a significant milestone, offering enhanced capabilities and a broader scope of protection for networks.
Delve into this comprehensive analysis to unravel the intricacies of NIDS, its advantages over NIPS, and its pivotal role in safeguarding the digital landscape.
NIDS stands as a testament to the relentless pursuit of innovation in cybersecurity. Its genesis lies in the foundation laid by NIPS, and through continuous technological advancements, it has evolved into a more robust and sophisticated solution. This journey from NIPS to NIDS is a chronicle of ingenuity and adaptation, driven by the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Differences between NIDS and NIPS
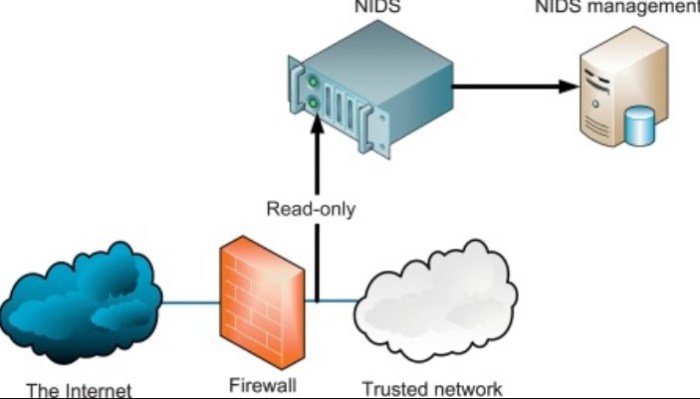
NIDS (Network Intrusion Detection System) and NIPS (Network Intrusion Prevention System) are both network security tools designed to protect against malicious activities. However, they differ in their approaches and capabilities.
Architectural Variations, Nids is an advanced version of nips.
NIDS operates in a passive monitoring mode, analyzing network traffic without actively interfering with it. It identifies suspicious activities and raises alerts, allowing administrators to investigate and respond.
NIPS, on the other hand, is an active system that can detect and prevent intrusions in real-time. It can block malicious traffic, drop suspicious packets, or take other actions to mitigate threats.
Detection Capabilities
NIDS focuses on detecting intrusions based on known patterns and signatures. It can identify attacks that match these predefined criteria.
NIPS, in addition to signature-based detection, can also use behavioral analysis to detect anomalous or suspicious activities that may not match specific signatures.
Examples
An example of a NIDS is Snort, which analyzes network traffic for known attack patterns and generates alerts.
An example of a NIPS is Suricata, which combines signature-based detection with behavioral analysis and can actively block malicious traffic.
Evolution of NIPS to NIDS

NIPS evolved from NIDS as network threats became more sophisticated. NIDS was initially limited to detecting known attacks, while NIPS emerged to address the need for proactive protection against evolving threats.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in intrusion detection techniques, such as behavioral analysis and machine learning, enabled NIPS to detect and prevent zero-day attacks and advanced persistent threats (APTs).
Case Studies
In 2010, the Stuxnet worm targeted industrial control systems. NIPS played a crucial role in detecting and preventing its spread by analyzing behavioral anomalies and blocking malicious traffic.
Comparative Advantages of NIDS over NIPS
NIDS offers several advantages over NIPS, including:
Enhanced Detection Capabilities
NIDS can detect a wider range of threats, including zero-day attacks and APTs, as it is not limited to signature-based detection.
Broader Scope of Protection
NIDS can monitor and protect multiple network segments and devices, providing a comprehensive view of network security.
Real-World Scenarios
In situations where proactive prevention is not feasible or may cause unintended consequences, NIDS can provide valuable insights into network activity and potential threats.
Integration of NIDS and NIPS for Enhanced Security
Integrating NIDS and NIPS within a security framework offers several benefits:
Complementary Capabilities
NIDS and NIPS complement each other by providing both detection and prevention capabilities, strengthening network protection.
Improved Threat Visibility
Integrating these systems allows for a more comprehensive view of network activity and threats, enabling faster and more effective response.
Case Studies
A study by Gartner in 2019 found that organizations that integrated NIDS and NIPS experienced a significant reduction in security incidents and improved overall network security posture.
Future Trends in NIDS Development: Nids Is An Advanced Version Of Nips.
NIDS technology is continuously evolving, driven by emerging trends:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms are being integrated into NIDS to improve threat detection and response capabilities.
Cloud-Based NIDS
NIDS solutions are moving to the cloud, providing scalability, cost-effectiveness, and easier management.
Predicted Capabilities and Applications
Future NIDS are expected to offer advanced features such as threat intelligence sharing, predictive analytics, and automated response capabilities.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key differences between NIDS and NIPS?
NIDS focuses on detecting intrusions and raising alerts, while NIPS actively prevents intrusions by blocking malicious traffic.
How does NIDS offer advantages over NIPS?
NIDS provides a broader scope of detection, including zero-day attacks, and allows for more flexible customization and integration with other security tools.
What are the benefits of integrating NIDS and NIPS?
Integration enhances network protection by combining the detection capabilities of NIDS with the prevention capabilities of NIPS, providing a comprehensive and layered defense.