Chapter 4 review arrangement of electrons in atoms – Embarking on Chapter 4’s exploration of electron arrangement in atoms, we delve into a fundamental concept that shapes the chemical properties of elements and underpins various atomic processes.
This chapter unravels the intricacies of quantum numbers, electron configuration, and periodic trends, providing a comprehensive understanding of how electrons are organized within atoms.
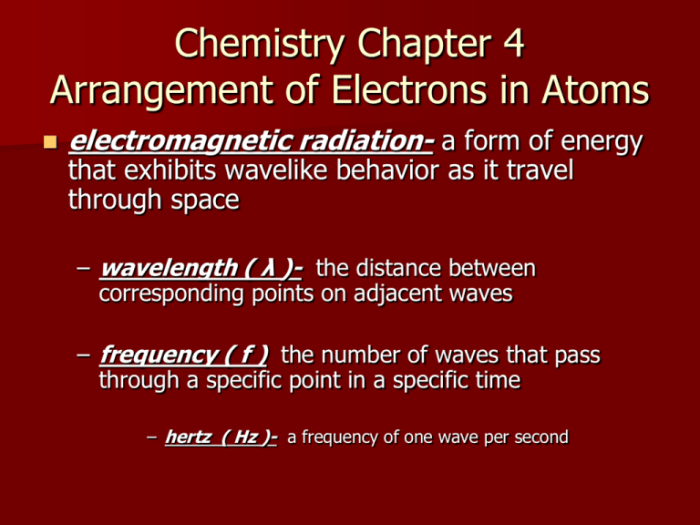
1. Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
Introduction

Electron arrangement in atoms is the spatial distribution of electrons around the nucleus. It plays a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of elements.
The arrangement of electrons within an atom’s orbitals influences its reactivity, ionization energy, and other atomic properties.
2. Quantum Numbers and Electron Configuration
Quantum numbers describe the properties of electrons within an atom. The four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms) define the energy level, shape, orientation, and spin of an electron.
Electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in the atomic orbitals, determined by the quantum numbers.
3. Aufbau Principle and Pauli Exclusion Principle, Chapter 4 review arrangement of electrons in atoms
The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy levels. The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
4. Periodic Trends in Electron Configuration
Electron configuration shows periodic trends across the periodic table. Elements in the same group have similar electron configurations, leading to similarities in their chemical properties.
Electron configuration influences the reactivity of elements, with elements in the same period generally having similar ionization energies.
5. Electron Configuration and Atomic Properties

Electron configuration affects various atomic properties, including ionization energy, electron affinity, and atomic radius.
Elements with low ionization energies tend to be more reactive, while elements with high electron affinities tend to be more electronegative.
6. Excited States and Electron Transitions: Chapter 4 Review Arrangement Of Electrons In Atoms
Excited states are energy levels higher than the ground state. Electrons can transition between energy levels by absorbing or emitting photons.
Electron transitions play a role in various atomic processes, such as light emission, absorption, and chemical reactions.
FAQ Resource
What is electron configuration?
Electron configuration refers to the distribution of electrons in atomic orbitals, which are specific regions around the nucleus where electrons are most likely to be found.
How do quantum numbers determine electron configuration?
Quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms) describe the energy, shape, orientation, and spin of electrons, and they govern the arrangement of electrons in orbitals.
What is the significance of the Aufbau principle?
The Aufbau principle dictates that electrons fill atomic orbitals in order of increasing energy, starting with the lowest energy level.